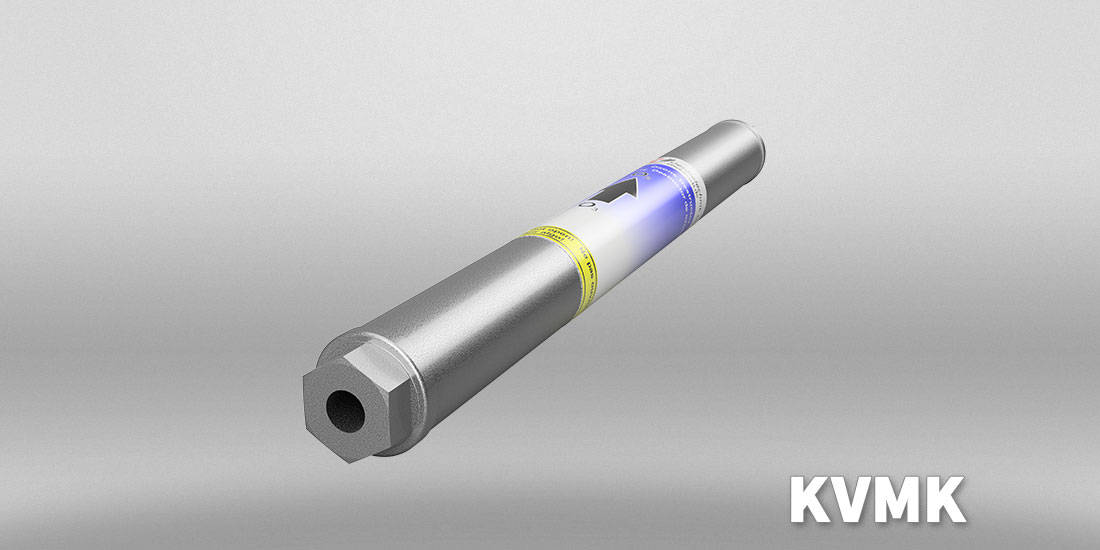
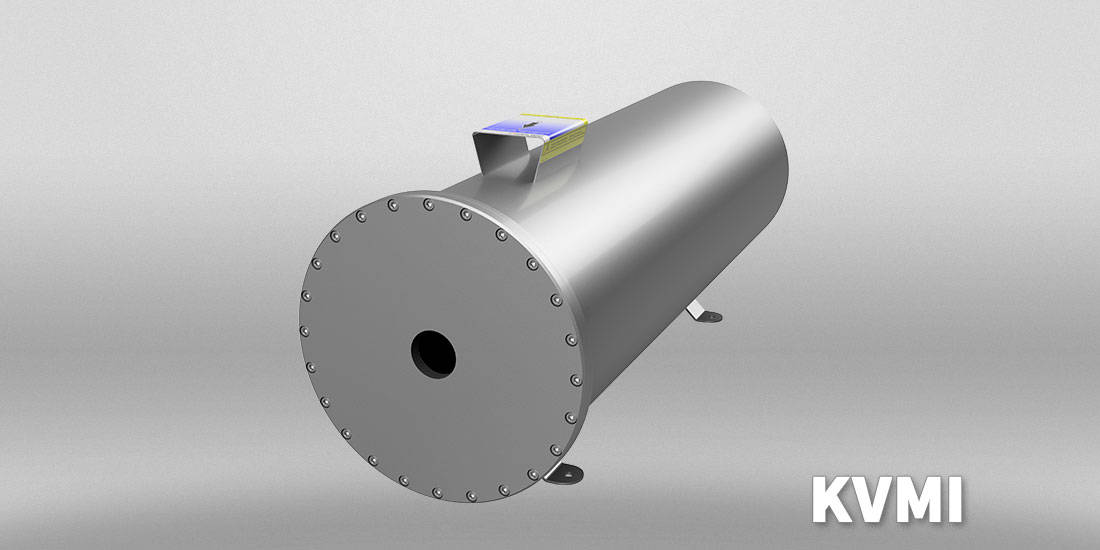
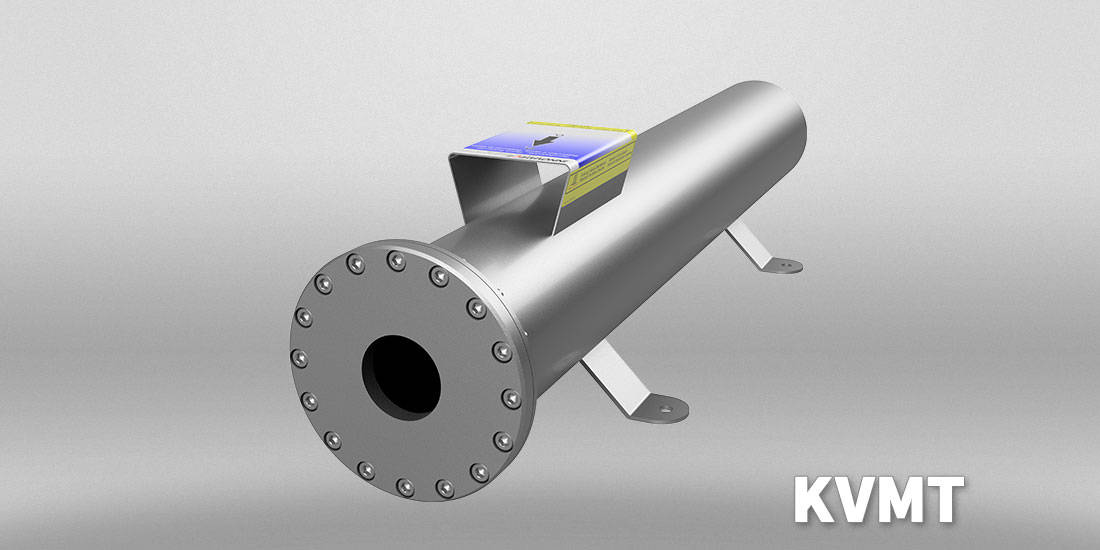
Residual ozone destructor according to the catalytic principle
The energy introduced during ozone production is released during the catalytic destruction of the residual ozone, which is therefore an exothermic catalytic reaction. Ozone gas enters (O₃ as a metastable agent) in the KVM ozone destructor and decomposes there with the release of heat into oxygen (O₂ electron pair-bound oxygen) as which it exits. The cold start catalyst is chosen so that a low back pressure is achieved at low velocity.
The thermal capacity is over 200 °C and the materials used are highly inert to the high oxidative affinity of the working gas. The catalyst is made out of a special activated noble metal mixture on an oxide ceramic substrate. The housing material is titanium-passivated stainless steel (material no.: 1.4571).
The Residual ozone destructors KVMK, KVM, KVMT, KVMENEW! and KVMI are characterized by a very long service lifetime of several thousand operating hours. After this time, a cost-effective regeneration at the manufacturer is possible.
Regulations
- Ozone destructors are required by law in most countries.
- In Germany, a guideline of 120 μg/m³, which is based on international limits is applicable (see BG-ETEM info sheet 526 07/2013).
Product Highlights
- Catalytic, exothermic reaction, ozone (O₃) will be decomposed to oxygen (O₂).
- Cold starting, no electrical connection or auxiliary energy required.
- Catalyst material based on noble metals on an oxide ceramic substrate.
- No dust creation as apposed to manganese dioxide.
- Service life: several thousand operating hours, depending on ozone concentration, moisture and particles in the gas.
- Envirommental friendly regeneration or upgrade possible.
- Housing material: Titanium stabilized and passivated stainless steel (1.4571 resp. AISI 316Ti).
- Thermal resistance: > 200 °C
- Operating temperature: 5…100 °C
- Special options possible on request
Applications Pharmaline
- Preferred for purest media applications (according GMP-C).
- Designed for high operating gas flow rates at low to medium ozone gas concentrations.
- I. e. electrolytic generated ozone (INNOVATEC-ELAP-series).
Applications KVM (standard)
- For all applications where large amounts of ozone are required and must be removed.
- I. e. Ozone generators principle of electric corona discharge (INNOVATEC-CMG-series).
Regeneration
- High quality standard regeneration by the manufacturer (according to workplace guidelines, incl. professional recycling).
- Guaranteed return of customer owned system (no exchange system, no cross contamination).
ozone destructor – pharmaline
Type | Housing | max. feed gas flow rate [Nm3/h] | max. ozone destruction rate [g O3/h] | Operating pressure [bar] | Test Pressure | Weight (packed) [kg] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KVMT-P7 | M | 7 | 21 | < 0.5 | +2 | 2.1 / (2.4) |
| KVMT-P15 | P | 15 | 45 | < 0.5 | +1 | 7.6 / (9.8) |
| KVMT-P30 | E NEW! | 30 | 90 | < 0.5 | +1 | 20.5 / (22.7) |
| KVMT-P45 | E NEW! | 45 | 135 | < 0.5 | +1 | 20.5 / (22.7) |
| KVMT-P65 | E NEW! | 65 | 195 | < 0.5 | +1 | 20.5 / (22.7) |
| KVMT-P90 | I | 90 | 225 | < 0.5 | +1 | 29 / (37) |
ozone destructor – standard
Type | Housing | Max. ozone destruction rate [g O3/h] | Max. feed gas flow rate [l/h] | Operating pressure [bar] | Test Pressure | Weight (packed) [kg] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KVMK 1-2 | K | 1 | 150 | < 0.5 | +1 | 0.6 / (0.7) |
| KVM 3-2 | M | 3 | 300 | < 0.5 | +1 | 2.3 / (2.6) |
| KVM 5-2 | M | 5 | 500 | < 0.5 | +1 | 2.3 / (2.6) |
| KVM 10-2 | M | 10 | 500 | < 0.5 | +1 | 2.3 / (2.6) |
| KVM 20-2 | M | 20 | 1.000 | < 0.5 | +1 | 2.3 / (2.6) |
| KVM 35-2 | M | 35 | 1.500 | < 0.5 | +1 | 2.3 / (2.6) |
| KVM 50-2 | M | 50 | 2.000 | < 0.5 | +1 | 2.3 / (2.6) |
| KVMT 70-2 | T | 70 | 3.000 | < 0.5 | +1 | 7.8 / (10) |
| KVMT 100-2 | T | 100 | 4.000 | < 0.5 | +1 | 7.8 / (10) |
| KVME 150-2 | E NEW! | 150 | 5.000 | < 0.5 | +1 | 21 / (23.5) |
| KVME 200-2 | E NEW! | 200 | 6.000 | < 0.5 | +1 | 21 / (23.5) |
| KVMI 250-2 | I | 250 | 16.000 | < 0.5 | +1 | 34 / (42) |
WEEE-Reg.-Nr. DE 84103047
KVM
The highest impact on the service life of ozone destructors have abrasive particles, high humidity and catalyst poison.
Usually the service life of an ozone destructor is between 8.000 and 12.000 operating hours.
Limits for the concentration of ozone in ambient air are ruled by various guidelines in many countries.
According to ZH 1/474 (2005) section 4.7.1 from the German Employer’s Liability Insurance Association an ozone destruction unit must ensure a limit of 0,02 mg/m³. The European Union guideline 2002/3/EG sets a limit of 180 µg/Nm³ (= 90 ppbv) for ozone emissions.
Until 2005 the limit for ozone concentration in companies was 90 ppb according to the German BG-ETEM (Infopaper 526 dated 07/2013). Exceeding that limit was not permissible. Meaning: The concentration of substances that can cause irritations and odors (like ozone) cannot exceed the maximum permissible value at any time. Currently there is no workplace exposure limit. The committee for hazardous materials is working on defining an occupational limit value. Until this will be released it is recommended to meet the international standard of 60 ppb (0,12 mg/m³).
The Swiss Clean Air Act limits the emission of ozone to 120 µg/m³ bzw. 60 ppb.
In the USA workplace-related rules according to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) and the National Institute of Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) is < 0,1 ppm (= 100 ppbv).